4.1 Overview of engine functions
This section explains a general overview of engine functions. Please refer to this section if you would like to know more about the internal process. The following diagram illustrates the SpeeDBee Synapse configuration.

4.1.1 Feature List#
This section describes the contents shown in the configuration diagram.
4.1.1.1 Core#
The core is the center of SpeeDBee Synapse that controls each feature. The core provides the following features.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Control Interface | Controls each feature of SpeeDBee Synapse. Accepts and processes requests from the WEBUI. The user will not use it directly. |
| Component API | Provides the APIs used by the component. Component developers need to use these APIs for programming. |
| Component Control | Controls the processing of components (a group of modules that enable data collection, processing, analysis, emission, etc.). The core automatically handles this internally. |
| Database Control | Controls the time series database on the SpeeDBee Synapse. The core automatically controls this internally. |
| License Control | Controls licenses. Controls the availability of SpeeDBee Synapse under the correct license. |
| SQL Web-API | Provides a Web-API that enables you to execute SQL against the time series database on SpeeDBee Synapse. For more information, see DB Query (SQL) and DB Query Service. |
4.1.1.2 Component#
A component is a group of modules that performs arbitrary processing in SpeeDBee Synapse. Using the components allows for the following.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Collection | You can collect data from a specific target. For more information, see Collector. |
| Data Analysis | You can analyze the collected data. For more information, see Logic (Realtime Analysis/Data Manipulation). |
| Event | Processes events according to the collected data. For more information, see Logic (Event). |
| Data Processing | You can process data into a specific format. For more information, see Serializer. |
| Data Output/Emission | You can output and emit data to a specific target. For more information, see Emitter. |
| Action | Performs any action. For example, it can execute OS commands or send mail. For more information, see Action. |
| System | Provides system-related functions. It is initially deployed and does not allow the user to add new instances. For more information, see System Component. |
| Custom | The user can develop components on its own. For more information, see Overview in Creating and Using Custom Components. |
4.1.1.3 WEBUI#
WEBUI provides a SpeeDBee Synapse screen for the user to interact with. WEBUI provides the following features:
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Authentication/Roles | Provides authentication features that allow SpeeDBee Synapse to be used by legitimate users. Roles can also be assigned according to User Roles. For more information, see User Management. |
| Core Process Control | Controls the core process. Enforces process control during user operations and core process errors. |
| Dashboard | Provides an interface that visually displays the data collection flow and allows for interactive customization. For more information, see Panel. |
| Configuration Information Management | You can manage configuration information on SpeeDBee Synapse. The information input by the user is maintained as a configuration file. |
| Operational Information Visualization | Displays operating status on SpeeDBee Synapse and components. For more information, see Status List. |
| Status History | Displays the component's operating status history. For more information, see Status Timeline. |
| Control Web-API | Provides a Web-API to control SpeeDBee Synapse. For more information, see Work with Control Program. |
| Data Monitor | You can view the collected data on the monitor. For more information, see Data Monitor. |
| Work with Graph | You can create a graph based on the collected data. For more information, see Work with Grafana. |
4.1.1.4 Database#
SpeeDBee Synapse includes a time series database. The time series database provides the following features.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Database API | Provides an API for working with the time series database. The user does not need to be aware of this API on SpeeDBee Synapse. |
| SQL | You can execute SQL against the time series database. For more information, see DB Query (SQL). |
| Time Series Data Processing (Register, Search, Delete, Storage) |
You can register, search, delete, and perpetuate the collected data. It is controlled by the core. |
4.1.2 Operating Specifications#
This section explains the operating specifications for SpeeDBee Synapse.
4.1.2.1 Basic Operation#
The basic operating specifications for SpeeDBee Synapse are as follows.

The table below shows the details of the processing executed in the above flow diagram.
- Basic Operation
| Processing | Description |
|---|---|
| WEBUI Start | Starts the WEBUI for SpeeDBee Synapse. An HTTP server runs internally. |
| Loading the Configuration of Restrictions and Available Functions | Loads configuration information. This includes information on the functions that will be enabled and the values of various restrictions. Basically, this does not involve any preparation or configuration by the user. |
| Startup Processing | Performs processing to start the core process and enable SpeeDBee Synapse. See below for details. |
| Core Process Monitoring Startup |
Starts core process monitoring. Monitors the core process status and restarts the core process when an error occurs. If the error persists, the system enters safe mode without starting the core process. |
| Signal Acceptance | Accepts signals from the OS. When a stop signal is received, the system transitions to the termination process. |
| WEBUI Stop | Stops the WEBUI. Terminates processes such as core process monitoring and performs cleanup operations for each process. |
- Startup Processing (Details)
| Processing | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Process Start | Starts the core process (background process) that will be the data engine for SpeeDBee Synapse. See below for details. |
| License Key Register | You can register a license key for SpeeDBee Synapse. The configuration license key in the WEBUI is applied and controls the features that can be used. |
| Environmental Parameter Configuration | Applies the database parameters configured in the WEBUI to the core process. |
| Configuration Information Verification | Verifies the components configured in the WEBUI and other information. Checks for configuration inconsistencies to ensure consistency is maintained. |
| Configured Component/Flowlink Register Request |
Applies components and flowlinks configured by the user to the core process. |
| Mode Judgment | Performs mode judgment. The modes include the following types. - Normal mode (This is the normal mode in which components are started in the startup process) - Safe mode (This mode is used when all components cannot be started during an error) |
| Start All Components Request |
Starts all registered components (except those with autostart disabled). This will put the data collection, processing, output, emission, and other processes into execution state. This processing is skipped in safe mode. |
The details of the core process start processing are as follows.
- Core Process Start (Details)
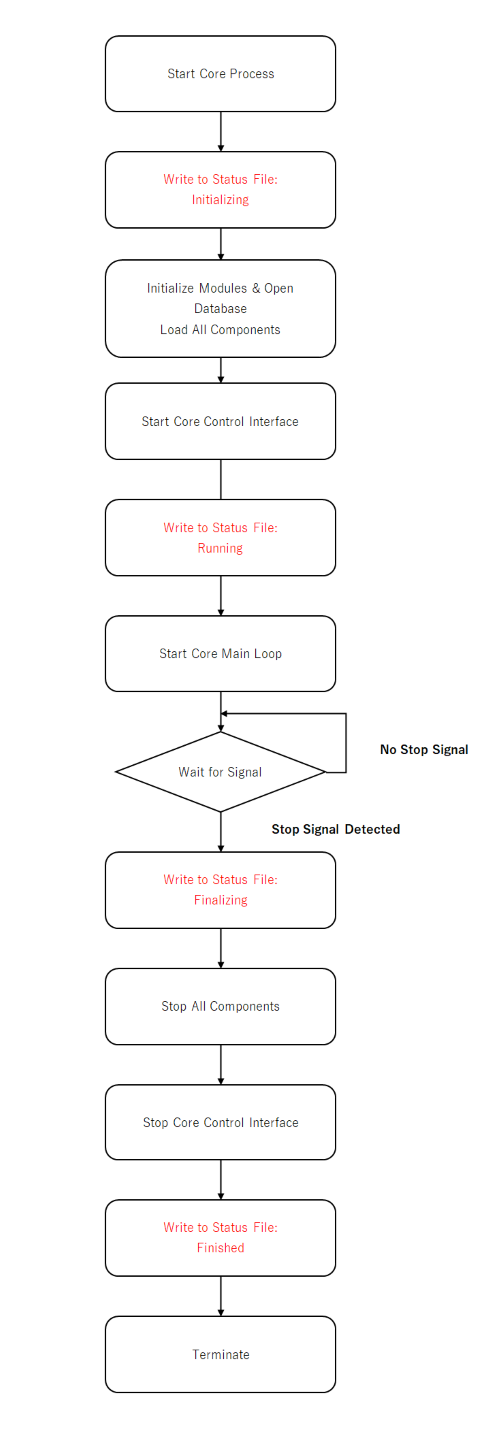
| Processing | Description |
|---|---|
| Record to Status File | Writes records to the status file for recording the start and stop status of the core. The status at this stage is Initializing. |
| Module Initialization and DB Opening Loading All Components |
Performs core module initialization. Within the initialization, the database is opened and all components are loaded. Problematic components are not loaded at this stage. Components that are deployed but cannot be initialized are excluded from being loaded. |
| Core Control IF Startup |
Enables an interface for controlling the core process. The system enters a state in which it can receive requests from the WEBUI. |
| Record to Status File | Writes records to the status file for recording the start and stop status of the core. The status at this stage is Running. When this status is recorded, it can be determined that this processing has started normally. |
| Core Main Loop Startup | Starts the main loop of the core. Executes various processes according to requests to the core control IF. |
| Signal Acceptance | Accepts signals from the OS. When a stop signal is received, the system transitions to the termination process. |
| Record to Status File | Writes records to the status file for recording the start and stop status of the core. The status at this stage is Finalizing. When this status is recorded, it can be determined that the termination process has been executed. However, since the next status is recorded after the termination process is completely completed, if the status remains in this state, it is determined that an error has occurred. |
| Stop All Components | Stops and destroys all components that are currently started. |
| Core Control IF Stop |
Stops the core control IF. External requests will no longer be accepted. |
| Record to Status File | Writes records to the status file for recording the start and stop status of the core. The status at this stage is Finished. When this status is recorded, it can be determined that the termination process has completed normally. The next time the core process is started, this status is referenced to determine the error during the previous startup. When it detects that a status other than Finished has been recorded, the core internal component registers an error status. If there is an error, you can view information on the Status Timeline. |
4.1.2.2 Normal Stop#
This section describes the operation at a normal stop. The chart below is an excerpt from the Core Process Start (Details). The red boxed area indicates important processing.
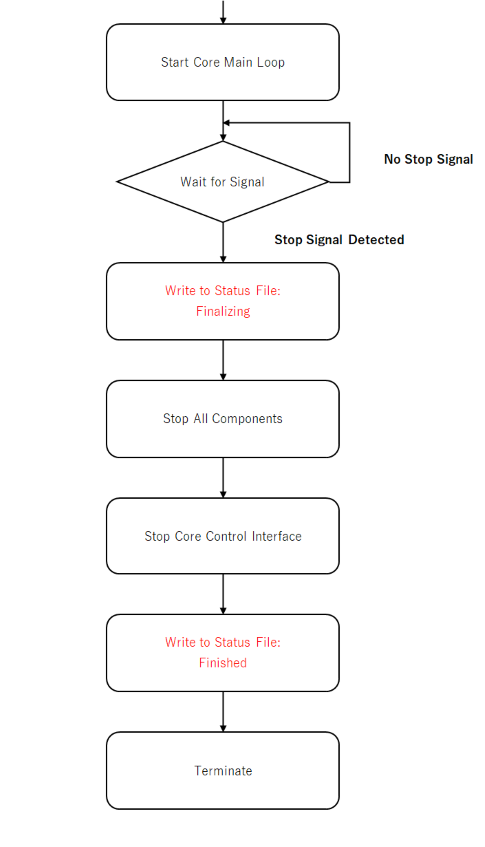
When the stop process is executed normally, a correct record is made in the status file. When Finished is recorded in the status file, it indicates that the stop process has been executed successfully. For more information, see Core Process Start (Details).
4.1.2.3 Abnormal Stop (e.g., power interruption)#
This section describes the operation at an abnormal stop. Abnormal situation means, for example, when the host machine stops due to power interruption while SpeeDBee Synapse is running.
- Determination of Core Process Abnormal Stop
As described in the explanation for normal stop operation, if SpeeDBee Synapse stops while it is running, a correct record will not be made in the status file. The next time the core process is started, the status file is determined and if a normal stop cannot be confirmed, the status is registered as an error status in the core internal. You can view error information on the Status Timeline.
- Determination of Database
If SpeeDBee Synapse experiences an abnormal stop while writing to the database, data loss in the database may occur depending on the timing of the stop. Data loss refers to the loss of some data while writing data stored in memory to storage because the data writing does not finish successfully due to a power interruption or other failure. The next time the core process is started, this determination will also be made internally. If an error is detected as a result of the determination, the status is registered as an error status in the core internal. You can view error information on the Status Timeline.
4.1.2.4 Operational Specifications Related to Data Collection#
In SpeeDBee Synapse, data collection in the component is the starting point for processing. However, there are some operational specifications that must be taken into account depending on the setting and timing of the operation, which are described below.
Timing of application of component configuration changes
When a configuration change is made, some changes are applied immediately, while others are applied after the component is stopped and restarted. In addition, some configurations have special timing for applying changes.
-
Item to which the new configuration is applied after component restart
-
Specific configuration for each component
Configuration items specific to each component will be reflected after the restart.
For example, if you add an address and save the configuration with a PLC Collector or other device, the configuration will not be applied if you do nothing. Once you stop the PLC Collector and restart it, it will operate with the new configuration reflected.
-
Items to which the new configuration is applied immediately after a configuration change
-
Flowlink Filters
- Flowlink Linking/Delete
-
Inport setting
-
Item to which the new configuration is applied at special timing after a configuration change
-
OUT Port
For OUT Ports, the new configuration is applied by creating a column after the configuration has been changed.
If a component creates columns at startup, the configuration will not be applied until restart. On the other hand, if a component is configured with regular expressions or other means and creates columns at a special timing, the configuration may be applied in the middle of the process.
For example, an MQTT Collector may not create columns until it receives data. In this case, if the OUT Port setting is specified by a regular expression or other means, the new configuration may be applied.
Note: If you want to ensure that the configuration is applied, restart the relevant component.
Data flow at the time of flowlink linking/delete
If you start a component that collects data and then link a flowlink to another component, the data before the link is made will not be collected.
In addition, if you delete a flowlink in the middle of the process, the relevant data will no longer flow to the destination of the link at the time of deletion, and the data processed by the relevant component will change. This is because even if the configuration is not changed, the data flowing through it will change, resulting in a change in the behavior of the operating components.
For example, assume that a PLC Collector and a Modbus Collector each have a flowlink to a JSON Serializer. In this case, if the flowlink between the PLC Collector and the JSON Serializer is deleted, the data referenced by the JSON Serializer will only be data from the Modbus Collector in the middle of the process.
Data Storage
For data acquired by the component that collects the data, storage is not created to the DB by default. Once the data is stored in the DB, you can use Grafana or the DB query service to view historical data for the storage period. If storage is not created, only the data currently kept in memory can be referenced.
If you want to create storage for these historical data for reference, please configure the settings in "storage setting" in "out port".
Delay time for data reference
The IN Port has a Delay Time setting.
This is the setting of how many seconds to delay the time range of the acquired data relative to the current time when referencing data.
This setting is intended to prevent the loss of data for which data collection has not been completed because data collection and data referencing are processed in parallel without synchronization.
Adjust this delay time when using data from components that require more time for data collection.
Depending on the component, it may be possible to guarantee data collection time and perform data referencing at intervals shorter than this delay. This is done automatically within SpeeDBee Synapse.
If you want to set the delay time, please refer to "in port".
Data when components stop
If the user stops a component, the most recent data from the operation in which the user stopped the component is not fully guaranteed.
For example, if a flowlink is linked from any collector to the serializer and the serializer is stopped, the serializer will operate to stop as quickly as possible. Therefore, while the serializer is stopped, data is not guaranteed since the data referencing process is not executed.
Do not inadvertently stop a component while the data you want to process is flowing.
4.1.2.5 Operational Specifications for Network Errors and Recovery#
This section explains the operational specifications for the occurrence of a network error on SpeeDBee Synapse and recovery from a network error.
Basically, components that use communication will reconnect to communication when a network error occurs.
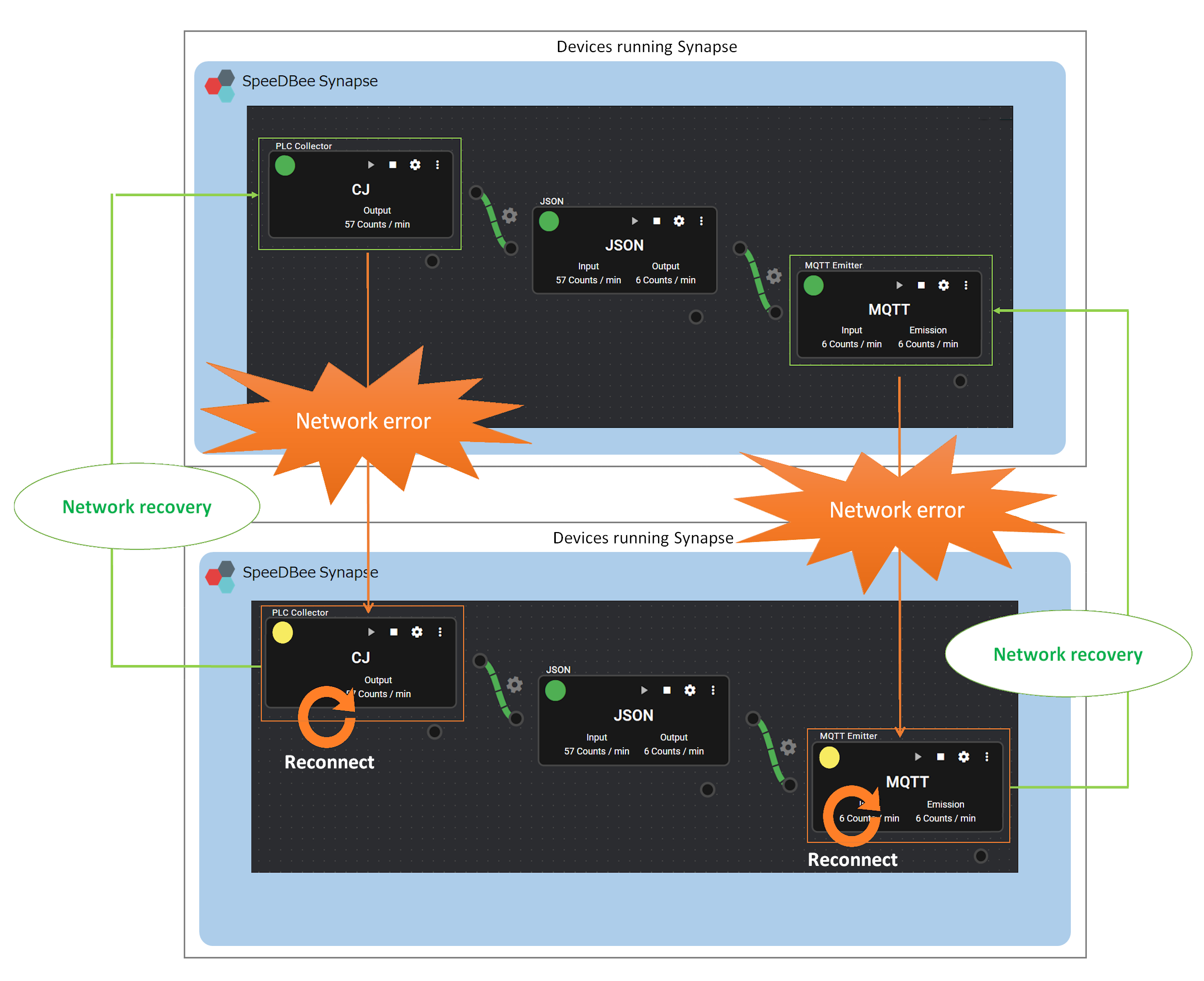
-
Components that collect data
Collector components that use communication will attempt to reconnect to communication if a network error occurs while collecting data. While an error occurs in communication, the network is in an error state and the status lamp changes to a Warning state. Data cannot be collected while a network error occurs. After the network in Operating machine is restored and reconnected successfully, data collection will resume normally.
The relevant components include:- PLC Collector
- Modbus Collector
- EtherNet/IP Collector
- VIDEO Collector
- MQTT Collector
-
Components that emit collected data
Action components and emitter components that use communication will attempt to reconnect to communication if a network error occurs during operation. While an error occurs in communication, the network is in an error state and the status lamp changes to a Warning state.
Action components
Data cannot be emitted while a network error occurs.
The relevant components include:- PLC Writing
- Modbus Writing
- EtherNet/IP Writing
- Send mail
Emitter components
Data cannot be emitted while a network error occurs. However, it is also possible to set a retry mode to re-emit data that has not yet been emitted.
The relevant components include:- Cloud Emitter (Azure)
- Cloud Emitter (AWS)
- FTP/FTPS/SFTP Emitter
- MQTT Emitter
FTP/FTPS/SFTP Emitters always attempt to re-emit data that has not yet been emitted.
For information on retry modes for other emitters, see the functional description of the relevant component.
When the communication process is carried out by a custom component or shell command generated by the user, the operation depends on the implementation.
If reconnection of communication is required when a network error occurs, the process to reconnect must be implemented in each implementation.