5.4 Global Variables
5.4.1 Overview of Global Variables#
Global variables store frequently changing data in the variables on the memory. These variables can be used in various functions of SpeeDBee Synapse, such as conversion, conditions, and arithmetic and conditional expressions of components, and SQL.
This prevents, for example, updates of conditional expression thresholds during system operation and registration of other data by specific data values.
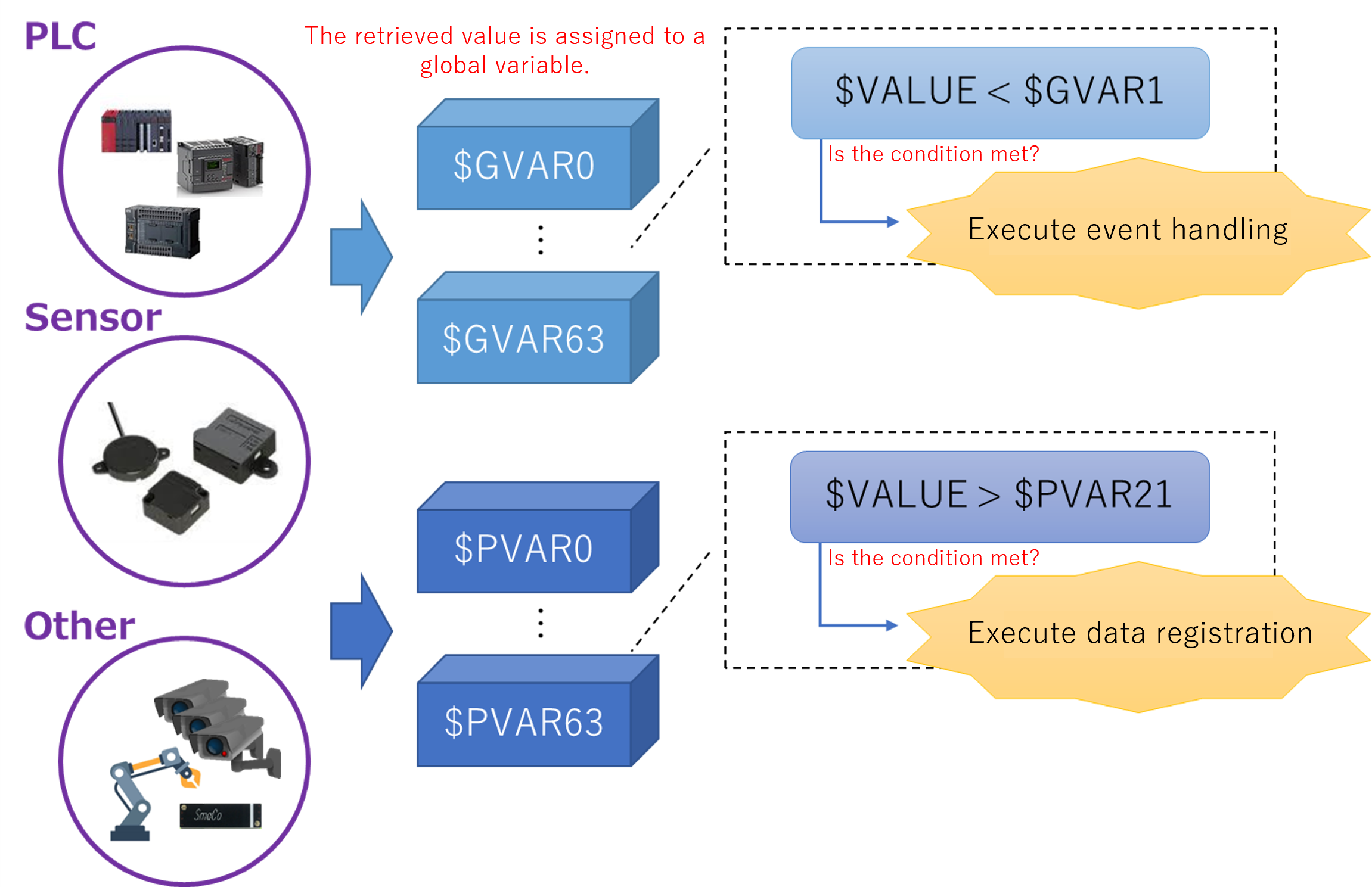
Global variables can be used in arithmetic expressions, conditional expressions, and SQL.
See here for information on arithmetic and conditional expressions.
See here for information on SQL.
5.4.2 Syntax of Global Variable#
There are two ways to specify a global variable: one is using the standard global variable and the other is using the persistence global variable. Both can use up to 64 variables.
With standard global variable, once the core of SpeeDBee Synapse is stopped (such as when an operating machine is restarted), the value is lost.
The persistence global variable allows for reading of the final value at next startup even when the SpeeDBee Synapse core has been stopped.
-
$GVAR0 to $GVAR63 (Global variable)
GVAR (global variable) is initialized to 0 each time you restart the SpeeDBee Synapse core. This remains 0 until a value is assigned.
-
$PVAR0 to $PVAR63 (Persistence global variable)
PVAR (persistence global variable) is initialized to 0 when the SpeeDBee Synapse core is started for the first time. When a value is assigned, the value is retained even after core restart.
To use the value assigned at previous startup when the SpeeDBee Synapse is restarted, use a persistence global variable.
-
Assign method
GVAR0 := $VALUENote: The "$" is not necessary at the beginning of a global variable to be assigned.PVAR15 := ($VALUE * 20)-
Notes on assignment in numeric conversions
When an assignment is specified as shown above, the value registered is $VALUE multiplied by 2. Note that the registered value changes.PVAR0 := $VALUE * 2 -
Notes on assignment in conditional expressions
You cannot specify only assignment in a conditional expression. An assignment within a conditional expression must be specified as a conditional expression as shown below.GVAR0 := $VALUEIn this case, the condition is satisfied if $VALUE is greater than 0. Assignment to GVAR0 is constantly done.0 < (GVAR0 := $VALUE)
-
-
Reference
$GVAR0 < $VALUENote: The "$" is added to the beginning of a global variable to be referenced.$PVAR15 > ($VALUE + 20)